Vasad
Background
The serious soil erosion and social problem of ravines attracted the urgent attention of the Government of India during the first five year plan. Consequently a chain of nine Central Soil & Water Conservation Research Centres were established by the Govt. of India. The Vasad Centre is one of the Centres established in May 1955. The Centre acquired 139 hectares farm along the Right Bank of river Mahi, which is representative of the problem of the area, in 1956. Subsequently the administrative control of the Centre was transferred to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research on 1st October 1967. On 1st April 1974 the Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute, Dehradun was formed and this Centre became one of the Research Centres of the Institute.

This Centre is situated at Vasad (Western Railway) on the National Highway No.8 (22o 27' 3" N and 73o 7' 0" E) in Anand district of Gujarat at a height of 34.18 m above mean sea level. R&D activities of the Centre focused on evolving strategies of soil and water conservation on watershed basis, tackling special problems of ravine reclamation. A complete package of practices has been developed for protection of ravines while putting it to productive utilization. Popularization of watershed management concept and technologies, strategies for ground water recharge and management, demonstration of technology and imparting training are important activities of the Centre. Experience of the research was made use of by the Ministries of Agriculture, Rural Development and Environment and Forests, and the Central and State departments in their development programmes. Success of the watershed management programme attracted many development agencies for collaboration and funding support. However, many gaps have remained unsolved and new issues have emerged which need further research and developmental attention.
The availability of new tools and procedures like GIS, remote sensing with better resolution and net working have opened new vistas for taking rapid R&D strides. The Centre represents agroecological region No.5 and 6, characterized with hot arid and semiarid eco region with red, lateritic and alluvium derived soils. The rainfall (Annual 840 mm) mostly occurs in four months of June, July, August and September. Daily evaporation ranges from 7 to 10 mm during dry hot months of March to May.
Mandate
- Appraisal of ravine problem and conservation of land and water resources along the Mahi and other river systems in Gujarat.
- Evaluation of hydrology and management for reducing sediment discharge and improving water regime and productivity in ravine lands.
- Evaluation and identification of suitable plant material for different land uses in ravine lands according to land capability.
- Development of suitable technology for increasing production from ravine lands.
- Monitoring changes in environment as affected by land use and management practices in ravine lands.
- Development of techniques for (a) Rain fed farming and (b) efficient water management in ravine lands.
- Development of techniques for stabilizing ravine lands.
- To set up demonstration projects for popularizing soil and water conservation measures in the region.
SCIENTISTS






Infrastructure
Buildings
The Centre has buildings covering an area of 2310 m2 and this includes main office campus, laboratory, library, residential quarters, garage, scooter shed and campus office, field laboratory, residential quarters and garages at the Research Farm.
Laboratory
 The centre has a laboratory equipped with most of the instruments required for the routine analysis of soil, water and plant samples. Special equipments like Yoder type wet sieving apparatus, Neutron moisture probe, are also available for supporting research and training in the area of soil and water conservation, land degradation and soil quality assessment, etc. The runoff and soil samples from the field plots and watersheds are being analyzed for various physical and chemical properties
The centre has a laboratory equipped with most of the instruments required for the routine analysis of soil, water and plant samples. Special equipments like Yoder type wet sieving apparatus, Neutron moisture probe, are also available for supporting research and training in the area of soil and water conservation, land degradation and soil quality assessment, etc. The runoff and soil samples from the field plots and watersheds are being analyzed for various physical and chemical properties
 Library
Library
The Centre has its own separate library to cater the needs of professionals engaged in soil and water conservation as well as watershed programme.
The library has 932 books and national and international journals.
Research Farm
The Centre has good laboratories and experimental research farm of 139 ha for conducting research, demonstration and training. The centre has a well equipped meteorological observatory with IMD certified instruments to observe weather parameters.
Vehicles
One Toyota Quails, one Swaraj Mazda, one Mahindra – Armada and two Tractors
Research
Research Achievements
Research achievements of the centre for past 50 years are presented under following broad groups
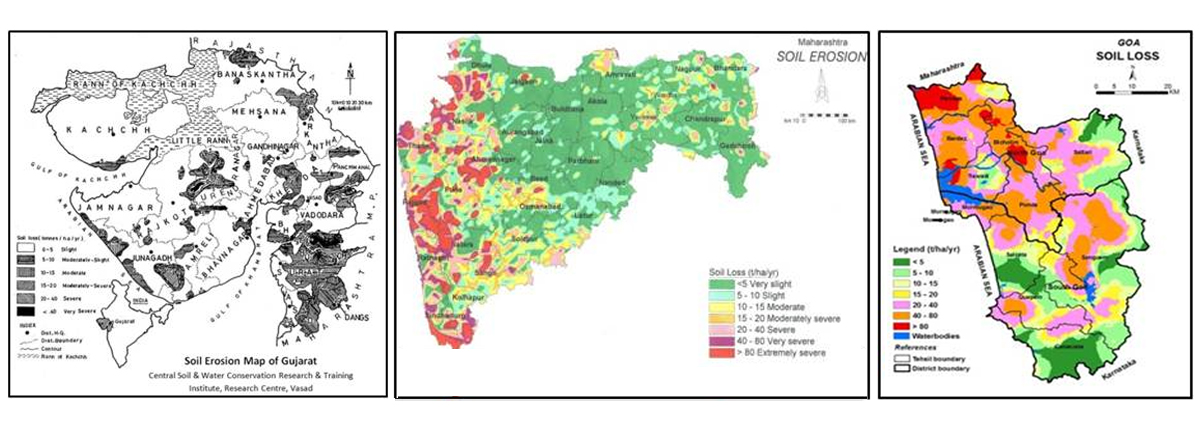
- Soil erosion maps of Gujarat, Maharashtra and Goa states were prepared jointly by this Centre and NBSSLUP, Nagpur showing areas under different soil loss classes
- Soil loss tolerance limit maps of Gujarat, Maharashtra and Goa states prepared
- Prepared the status report on soil erosion in coastal belt of India with information covering the coastal Gujarat
Research highlights
 Various parameters of Universal Soil Loss Equation were determined and using this information from different regions, soil erosion maps of Gujarat, Maharashtra and Goa have been prepared.
Various parameters of Universal Soil Loss Equation were determined and using this information from different regions, soil erosion maps of Gujarat, Maharashtra and Goa have been prepared.- The best preventive method against the march of ravines to the table lands is laying out the contour and peripheral bunds of 0.93 m2 cross section with pipe outlets to dispose of excess runoff water. The bunds should be sodded with Dichanthium annulatum and Cenchrus ciliaris grasses. This information has helped in its introduction all over the State.
 Gully plugs of 1.1 m2 cross section are used for control of erosion in small gullies. Small gullies can be reclaimed by clearing and minor leveling and putting series of contour bunds at 0.9 m vertical interval, medium gullies can be reclaimed by clearing, leveling the bed, construction of series of composite check dams of 1.2 m height and bench terracing the side slopes. These specifications have been used as benchmark by various development agencies in the state.
Gully plugs of 1.1 m2 cross section are used for control of erosion in small gullies. Small gullies can be reclaimed by clearing and minor leveling and putting series of contour bunds at 0.9 m vertical interval, medium gullies can be reclaimed by clearing, leveling the bed, construction of series of composite check dams of 1.2 m height and bench terracing the side slopes. These specifications have been used as benchmark by various development agencies in the state.- Closure of ravines assisted with conservation measures and planting of tree species like Acacia nilotica, Prosopis cineraria, Azadirachta indica etc. transform the degraded ravines into a good natural forest in 20-30 years. In areas with low moisture regime, tropical thorn forest is formed. In higher soil moisture regime, tropical dry deciduous forests are formed.
- Deep gullies in Mahi ravine areas can be reclaimed with low inputs. The technology has been adopted by Tree Grower’s Cooperatives in Gujarat and other parts of the country.
 Amongst the various grasses tried, it has been observed that Chrysopogon fulvus (1/IGFRI), Eulaliopsis binata (CSERI), Cenchrus ciliaris (379/CSWRI), Cenchrus ciliaris (3108/IGFRI) and Cenchrus ciliaris (380/CSWRI) are most suitable for Vasad region giving annual green grass yield of more than 15 t/ha. Yield potential of grasses has been used in their introduction in the watershed programmes.
Amongst the various grasses tried, it has been observed that Chrysopogon fulvus (1/IGFRI), Eulaliopsis binata (CSERI), Cenchrus ciliaris (379/CSWRI), Cenchrus ciliaris (3108/IGFRI) and Cenchrus ciliaris (380/CSWRI) are most suitable for Vasad region giving annual green grass yield of more than 15 t/ha. Yield potential of grasses has been used in their introduction in the watershed programmes.- Dendrocalamus strictus can be introduced in ravine beds with check dams. The returns are Rs. 25000 – 50000 (2012 prices) per hectare per annum after 7th year and continue till bamboo flowers in 40-50 years. This species have been introduced in Mahi ravine area.
 The main crops recommended in Vasad region for summer are pearl millet, green gram, groundnut, maize and fodder pearl millet under irrigated conditions. The main kharif crops are pearl millet, tobacco, cowpea, maize, castor, pigeon pea, cotton and sorghum. The rabi crops are wheat, mustard, rabi sorghum and maize. This has helped designing cropping programme on reclaimed Mahi ravine land.
The main crops recommended in Vasad region for summer are pearl millet, green gram, groundnut, maize and fodder pearl millet under irrigated conditions. The main kharif crops are pearl millet, tobacco, cowpea, maize, castor, pigeon pea, cotton and sorghum. The rabi crops are wheat, mustard, rabi sorghum and maize. This has helped designing cropping programme on reclaimed Mahi ravine land.- Under irrigated conditions, plantation of horticultural crops like lemon is economical in gully beds and terraces. This information has helped for profitable development of medium gullies in Mahi ravines.
- The successful fodder grasses in Vasad ravine conditions are Cenchrus cilairis, Dichanthium annulatum, Chrysopogon fulvus and Cenchrus setigerus. The fodder yields range from 4 to 10 t-1ha-1annum-1. These grass species have been successfully introduced in operational research projects.
- Effect of growing trees such as Eucalyptus tereticornis and Leucaena leucocephala on agricultural field boundary with tobacco crop revealed that there was reduction in tobacco yield by more than 50% up to 6 m distance as compared to no tree on boundary. This system has been advocated to farmers in Mahi ravines during lab to land programme.
- Stubble Mulch Farming Tillage (SMFT) and Ridge Farming Tillage (RFT) were found to be the best tillage practices in terms of yield of pearl millet+pigeon pea and cowpea+castor intercropping and controlling runoff and soil loss.
 Study on vegetative barriers in Vasad conditions revealed that Dichanthium annulatum produced minimum runoff (32.4%) and soil loss (2.7 t/ha) as compared to other barriers like Vetiveria zizaniodes (45.5% run-off and 5.02 t/ha soil loss), Cenchrus ciliaris (46.3%, 4.46 t/ha), Aloe barbadense (52.2%, 6.69 t/ha). This revalidates wider replication of Dichanthium annulatum as vegetative barrier in varied conditions.
Study on vegetative barriers in Vasad conditions revealed that Dichanthium annulatum produced minimum runoff (32.4%) and soil loss (2.7 t/ha) as compared to other barriers like Vetiveria zizaniodes (45.5% run-off and 5.02 t/ha soil loss), Cenchrus ciliaris (46.3%, 4.46 t/ha), Aloe barbadense (52.2%, 6.69 t/ha). This revalidates wider replication of Dichanthium annulatum as vegetative barrier in varied conditions.- Socio-economic analysis of Navamota and Rebari watersheds in Gujarat revealed benefit- cost ratio of crop production sector to be 2.65 - 2.67 based on 12% discount rate and 30 years period of analysis. The average farm investment increased by 3 to 5 times. The over-all benefit-cost ratio of the project worked out to be 2.00. This reaffirms the viability of soil and water conservation technologies.
- Economic evaluation of a mixed plantation consisting of Acacia nilotica with Cenchrus ciliaris and Dichanthium annulatum raised in deep ravines revealed a benefit-cost ratio of 1.38 and internal rate of return of 15% with a payback period of 15 years. This economically viable system has been used in common land management in Integrated Wasteland Development Project, Antisar.
- Economic evaluation of afforestation conservation measures in deep ravines of Mahi at 1995-96 prices revealed an internal rate of return of 18% with a payback period of 14 year and an annual payout of Rs. 11284/ha at constant prices. The information has been successfully used by National Tree Growers’ Cooperative Federation in Gujarat.
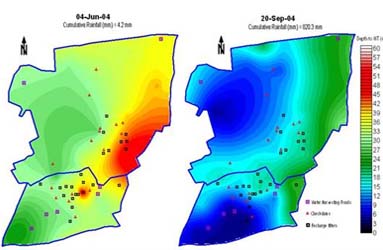
- Water storage structures like check dam, pond introduced in the IWDP, Antisar increased groundwater recharge, thereby successfully mitigating drought effect in the watershed. The conserved excess water was used to save kharif cops in absence of rains. The groundwater recharged also helped increase water table and improve water quality after monsoon as compared to pre-monsoon.
- The overall impact of informal trainings was measured with the help of the training index and the actual impact of informal trainings was 30.1% improvement in knowledge, symbolic adoption and adoption behaviour of rural farmers.
Present Research projects
- Effectiveness of vegetative filter strips in preventing soil and nutrients losses
- Erosion-productivity relationships for evaluating vulnerability and resiliency of soils under different agro-climatic regions of India
- Enhancing productivity of ravine lands by plantation of A. sapota with intercropping systems
- Evaluation of hydrological behavior and production potential of recommended land use system/ practices under different agro-ecological regions of India
- Hydrological implication of sequential alteration of land use covers in a ravinous catchment
- Hydrologic and economic evaluation of Bamboo plantations in gullied lands under major ravines of India
- Design and development of site specific artificial groundwater recharge filters
- Field evaluation of design of trenches under different agro-climatic regions
- Multiple criteria decision for identifying suitable Integrated Farming Systems in different agro-ecological regions for optimizing resource conservation and productivity
- Evaluation of institutional arrangements and impact of community based water storage structures in different agro-climatic zones of India
- Post-adoption behaviour of farmers towards soil and water conservation technologies of watershed management
Training
Human Resource Development/Training
Training facilities
 The centre has a training-cum-seminar room with modern amenities such as multimedia projector, VCD player, internet and a digital camera. Training is being imparted on the following areas to Govt. officials, students and farmers from time to time.
The centre has a training-cum-seminar room with modern amenities such as multimedia projector, VCD player, internet and a digital camera. Training is being imparted on the following areas to Govt. officials, students and farmers from time to time.
- Soil and water conservation
- Integrated watershed planning, management, monitoring and evaluation
- Hydrologic monitoring, water harvesting, drainage line treatment and ground water recharge and quality aspects
- Integrated Wasteland Development and Drought Prone Area Development
- Participatory Rural Appraisal in watershed development
- Economic analysis of watershed development interventions
- Short practical training programmes of nearly one-month duration in soil and water conservation in ravines are being organized for graduate students of Agricultural Engineering of Agricultural Universities in Gujarat and outside.
- Weekly training programmes being imparted to officials of Gujarat State Land Development Corporation (GSLDC) have benefited them in carrying out watershed programmes in Gujarat.
- Groups of farmers have been trained in one-day camps at the Centre under the auspices of the IWDP, Antisar Project.
- One week refresher course for junior level Govt. officers from Agriculture, Soil conservation, Forest, Agricultural Engineering and other Departments, WDT members etc. of Govt. & NGOs
- Exposure Camp/Visit (1 day) for farmers and
- One week training programme for MDT/WDT staff members of GSWMA, Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Training module for 6 days Training Programme on Bamboo Plantation Based Technological Interventions for Reclamation and Productive Utilization of Degraded Lands
| Days | Topics covered |
|---|---|
| Day -1 | Degraded lands (types, extent, classification) and their reclamation measures (engineering, vegetative and bio engineering measures)-an overview; use of advance tools(RS, GIS, GPS) for planning bamboo plantation in degraded lands |
| Day -2 | Environmental and soil suitability classification for bamboo plantation in ravine lands; Suitable bamboo species for ravine lands, their silvicultural practices; bamboo regeneration techniques; bamboo nursery management practices |
| Day -3 | Filed visit- Exposures to bamboo nursery practices Filed visit- Exposures to bamboo plantation based interventions for ravine reclamation |
| Day -4 | Planning, design, estimation, layout and execution of staggered trenches, earthen gully plugs/bori bunds, supported by bamboo plantation in ravine lands |
| Day -5 | Planning, design, estimation, layout and execution of peripheral bunds supported by bamboo plantation and check dams for bamboo plantation in ravine lands |
| Day -6 | Silivcultural practices of bamboo plants in ravine lands; growth, production, economics of bamboo in various bamboo based interventions; uses of bamboo and its marketing for livelihood security, Monitoring & impact of bamboo plantation based interventions on natural resource conservation |
| Course fee for 6 days’ training programme per participant Rs. 5363/- | |
Training module for 3 days Training Programme on Bamboo Plantation Based Technological Interventions for Reclamation and Productive Utilization of Degraded Lands
| Days | Topics covered |
|---|---|
| Day -1 | Degraded ravine lands- an overview; suitable bamboo and grass species for ravine lands and their regeneration, nursery techniques & practices. Filed visit- Exposures to bamboo plantation based interventions for ravine reclamation |
| Day -2 | Planning, design, estimation, layout and execution of Bamboo based interventions for reclamation and productive utilization of degraded gully beds, heads and banks |
| Day -3 | Silivcultural practices of bamboo plants in ravine lands; impact of bamboo plantation based interventions on natural resource conservation (soil, water, nutrients carbon sequestration) , economics, marketing and livelihood security |
| Course fee for 3 days’ training programme per participant Rs. 3463/- | |
Research Farm
 The centre has a research farm with well equipped infrastructural facilities for conducting the field experiments, demonstration plots, runoff plots and small watershed studies.
The centre has a research farm with well equipped infrastructural facilities for conducting the field experiments, demonstration plots, runoff plots and small watershed studies.
Two tractors with farm equipments are used for farm operations.
The details of research farm area is given below
| Details | |
|---|---|
| Average rainfall (mm) | 839 |
| Gross area (ha) | 139 |
| Cultivated area (ha) | 11.0 |
| Forest area (ha) | 121.7 |
| Area under road, culvert and others (ha) | 6.3 |
| Source of irrigation | Tube well |
Meteorological Observatory
The centre has a well equipped meteorological observatory with IMD certified instruments to observe weather parameters
 Field/runoff plots
Field/runoff plots
This centre is also equipped with hydrological devices like mechanical stage level recorders, H-Flumes, Coshocton silt samplers, multi-slot devisors and number of self recording gauging stations (runoff plot, field plots, micro watershed and small watersheds) for measuring runoff, soil loss and nutrient loss under different situations in the region.
Collaboration
Integrated Watershed Management
- Completed Integrated Watershed Development Programmes in Navamota Watershed (Dist. Sabarkantha) and Rebari Watershed (Dist. Panchmahals)
- Successfully demonstrated the concept of participatory watershed management at Antisar Watershed in Kapadwanj taluka of Kheda district, Gujarat under IWDP
- Vejalpur-Rampura watershed located in Kapdwanj Taluka of Kheda district of Gujarat was successfully developed by CSWCRTI, RC, Vasad through transfer of various watershed development interventions under NWDPRA scheme funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Govt. of India
Deep Ravine Reclamation
- Transferred treatment package for deep ravine reclamation in Sarnal, district Kheda, Gujarat to National Tree Growers’ Cooperative Federation (NTGCF), Anand


Collaboration/linkages
- This centre had technical collaboration with National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning (NBSSLUP), Nagpur for the preparation of soil erosion rate map of Gujarat, Maharashtra and Goa states
- Collaboration with Gujarat State Land Development Corporation, Gujarat State Forest Department, District Rural Development Agency (DRDA), Anand, Baroda, Kheda and Sardar Sarovar Narmada Nigam Limited, Gandhinagar
- This centre has also collaborated with National Tree Growers’ Cooperative Federation (NDDB) and other voluntary organizations engaged in wasteland development works of the state.
- The Centre has extension linkages with different extension agencies of the state and workers of these organizations visit the centre from time to time to see research achievements in the fields of soil and water conservation engineering, agronomy and forestry for reclamation of the different ravine lands and get educated for proper planning and execution for the development of the different wasteland development works in which they are engaged
Consultancies
Completed
- Monitoring sediment and runoff yield from treated watersheds. (1993-1996) Sardar Sarovar Narmada Nigam Limited (SSNNL), Gandhinagar
- Preparation of Micro-plan for Design and Estimate of Soil and Moisture Conservation Interventions of Development Units 4, 10 and 13 in Attapadi Wasteland Project, Agali, Attapadi, Palakkad, Kerala State, at Attapadi Hill Area Development Society, Palakkad in Kerala State. (2002)
- Rainfall, Runoff and Sediment yield measurements in catchment area of Sardar Sarovar Project. (2004-2009) Sardar Sarovar Narmada Nigam Limited (SSNNL), Gandhinagar
- Monitoring treated catchment for their hydrological behavior in terms of runoff and soil loss in SSP, Maharashtra. (2006-2008). Office of the Chief Conservator of Forests (T), Dhule, Maharshtra, Ram Manohar Lohia Marg, Near SRPF Ground, Dhule – 424 001 (Maharashtra)
- Impact Evaluation Studies (IES) of two watersheds treated during five year plan under NWDPRA, Samlod District Bharuch and Nani Vavdi, District - Ahmedabad in Gujarat, NRAA, New Delhi
- ICAR Support to Rwanda to Assist ISAR in the Adaptation of Indian Experiences in Integrated Management of Watersheds, ISAR, Kigali, Rwanda
On going
- Mid-term evaluation of NABARD supported Holistic Watershed Development Programme (NHWDP), Maharashtra. National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), Maharashtra Region 54, Wellesley Road Post bag No.5 Shivaji Nagar, Pune- 411005



